Volume 12
January - December, 2018

Article 1
Fluid Density and Impact Cavity Formation
by Lin, G., Michelin, A., Siriwanna, D., Tanalikhit, P.

Article 1
Fluid Density and Impact Cavity Formation
by Lin, G., Michelin, A., Siriwanna, D., Tanalikhit, P.
Characteristics of the impact cavity formed when a steel ball is dropped into aqueous solutions of densities ranging from 0.98 g·cm-3 to 1.63 g·cm-3 were investigated. A high-speed camera was used to record the formation and collapse of the cavity. The results showed cavity diameter, volume, and pinch-off time are independent of fluid density, on average. There was an unexplained reduction in cavity formation for densities of 1.34 g·cm-3 and 1.45 g·cm-3.
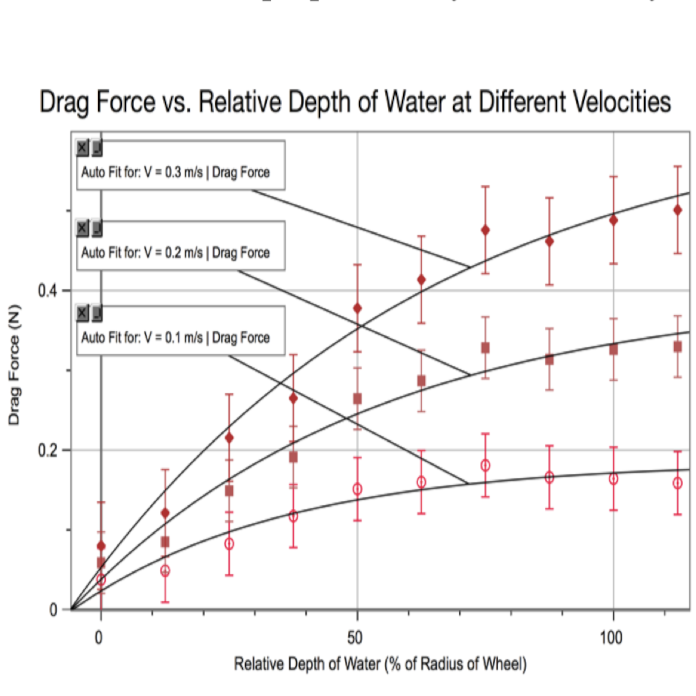
A model car was pushed and then allowed to freely decelerate through water with depths ranging from 0.0 to 4.0 cm. Water depths that submerged only the wheels, not reaching the body of the car, were tested. It was shown that the rate of increase of drag force decreases as depth of water increases, and the drag force is proportional to the velocity of the car. The drag force was almost constant for water depths above 75% of the wheel’s radius, for a given velocity.
