Volume 11
January - December, 2017

The effects of sound stimulation on mitosis, the extent of mitotic activity, and the characteristics of chromosomes and nuclei during mitosis in Allium cepa (onion) root tips were studied. Growing chambers were designed to allow one group of onion roots to grow with regular exposure to sound at a frequency of 5,000 Hz and an intensity of 75.9 dB. Another group of onions were grown without sound stimulation and served as the control group. It was shown that exposure to sound had adverse effects on Allium cepa root growth and mitotic activity. Sound-stimulated onions grew fewer and shorter roots and retained less mass. Analysis of mitotic abnormalities found in sound-stimulated root cells showed that sound exposure interfered with normal chromosome activity during mitosis, suggesting mitotic instability.
Clitoria ternatea, or butterfly pea, is an easily accessible Asian flower that can function as a pH indicator. A method of preparing the butterfly pea flower indicator is described, then a pH color scale between pH 2 and 12 is shown. The indicator is stored over 8 days and tested to determine its reliability over time. It is concluded that the indicator solution has an effective shelf life of less than 5 days. A method for creating pH paper is then described and its pH color scale is shown. The change in the pH color scale is shown while storing the pH paper at room temperature and under refrigeration over a period of 10 days. It is found that storing pH paper in a refrigerator extends its reliability.
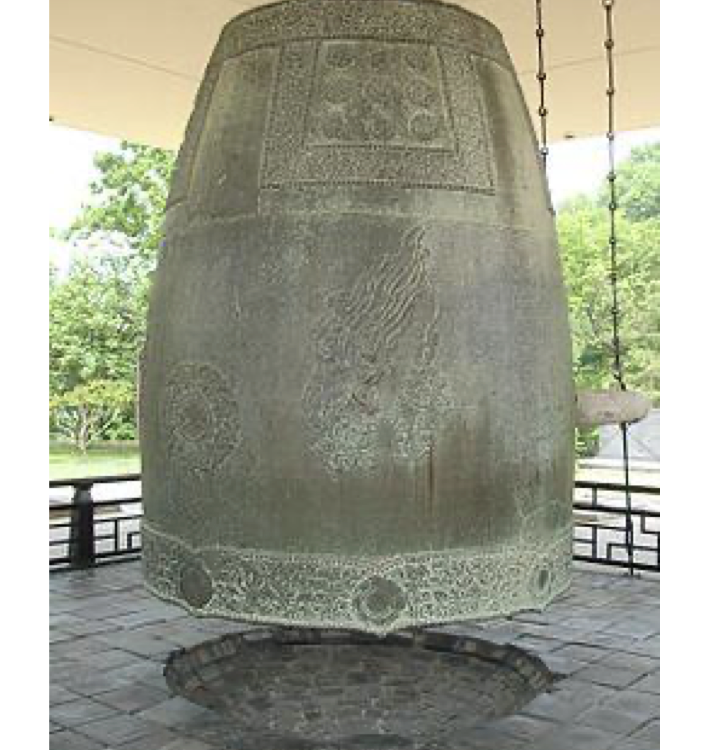

Traditional Korean bells are installed above a shallow well with a gap between the bell and the ground, effectively creating a Helmholtz resonator. During installation, the size of the well and the gap is traditionally adjusted, through trial and error, until the Helmholtz frequency matches the fundamental frequency of the bell. Here, the frequency of the Helmholtz resonator in Korean bells was investigated. Models of the resonator with various dimensions were built, and their resonant frequency measured. An equation for the Helmholtz frequency of the resonator was developed, which predicts the frequency of Korean bells within 4%. The equation can be used by traditional Korean bell installers to design the well and gap to ensure that the Helmholtz frequency of the resonator matches the fundamental frequency of the bell.

Article 4
Paddle Angle and Ball Spin in Table Tennis
by Broca, B., Chen, A., Kraivisitkul, N., Poprom, P.

Article 4
Paddle Angle and Ball Spin in Table Tennis
by Broca, B., Chen, A., Kraivisitkul, N., Poprom, P.
The relationship between the impact angle of a table tennis ball with respect to the paddle and angular velocity of the ball leaving the paddle was investigated. A table tennis ball was dropped onto a paddle oriented at impact angles ranging from 10° to 80°. It was found that the sine of the impact angle is proportional to the angular velocity of the ball as it leaves the paddle for all impact angles tested.
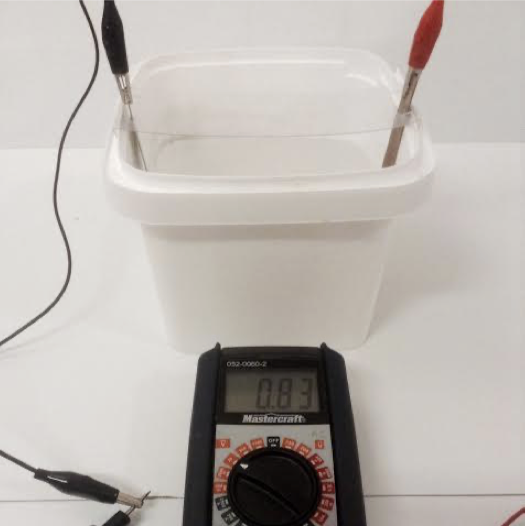

Metal-air batteries consist of a solid metal anode and an oxygen cathode of ambient air, typically separated by an aqueous electrolyte. Here, simple saltwater-based models of aluminum-air and zinc-air cells are used to determine the differences between theoretical cell electric potentials and experimental electric potentials. A substantial difference is observed. It is also found that the metal cathode material is crucial to cell electric potential, despite the cathode not participating in the net reaction. Finally, the material composition of the cathode appears to have a more significant impact on cell potential than the submerged surface area of the cathode.
